Inorder Successor in BST
Created: August 22, 2019 by [lek-tin]
Last updated: August 22, 2019
Given a binary search tree and a node in it, find the in-order successor of that node in the BST.
The successor of a node p is the node with the smallest key greater than p.val.
Example 1
Input: root = [2,1,3], p = 1
Output: 2
Explanation: 1's in-order successor node is 2. Note that both p and the return value is of TreeNode type.
Example 2
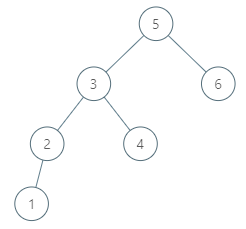
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,null,1], p = 6
Output: null
Explanation: There is no in-order successor of the current node, so the answer is null.
Note
- If the given node has no in-order successor in the tree, return null.
- It’s guaranteed that the values of the tree are unique.
Solution
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
# Time: o(h)
class Solution:
def inorderSuccessor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
if not root:
return None
if root.val > p.val:
# Root is greater than p, so traverse down to left substree
succ = self.inorderSuccessor(root.left, p)
# If not succ is found, return root; Otherwise return the smaller succ
return root if succ == None else succ
else:
# Search in right subtree only, as the successor definitely doesn't exist in the left subtree
return self.inorderSuccessor(root.right, p)
# time: `O(n)`
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
class Solution:
def inorderSuccessor(self, root: 'TreeNode', p: 'TreeNode') -> 'TreeNode':
stack = []
found = False
while root or stack:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
if found:
return stack[-1]
found = p.val == stack[-1].val
root = stack.pop().right
return None