Number Complement
Created: May 5, 2020 by [lek-tin]
Last updated: May 5, 2020
Given a positive integer, output its complement number. The complement strategy is to flip the bits of its binary representation.
Example 1:
Input: 5
Output: 2
Explanation: The binary representation of 5 is 101 (no leading zero bits), and its complement is 010. So you need to output 2.
Example 2:
Input: 1
Output: 0
Explanation: The binary representation of 1 is 1 (no leading zero bits), and its complement is 0. So you need to output 0.
Note:
- The given integer is guaranteed to fit within the range of a
32-bitsigned integer. - You could assume no leading zero bit in the integer’s binary representation.
- This question is the same as 1009: https://leetcode.com/problems/complement-of-base-10-integer/
Hint:
x is some bit
0 xor x = x
1 xor x = 1 − x
Solution (bit by bit 1)
Java
class Solution {
public int findComplement(int num) {
int todo = num, bit = 1;
while (todo != 0) {
// flip current bit
num = num ^ bit;
// prepare for the next run
bit = bit << 1;
todo = todo >> 1;
}
return num;
}
}
Time: O(1)
Space: O(1)
Solution (bit by bit 2)
Java
class Solution {
public int findComplement(int num) {
if (num == 0) return 1;
int ans = 1;
while (ans - 1 < num) {
ans <<= 1;
}
return ans - 1 - num;
}
}
Time: O(1)
Space: O(1)
Solution (Compute Bit Length and Construct 1-bits Bitmask)
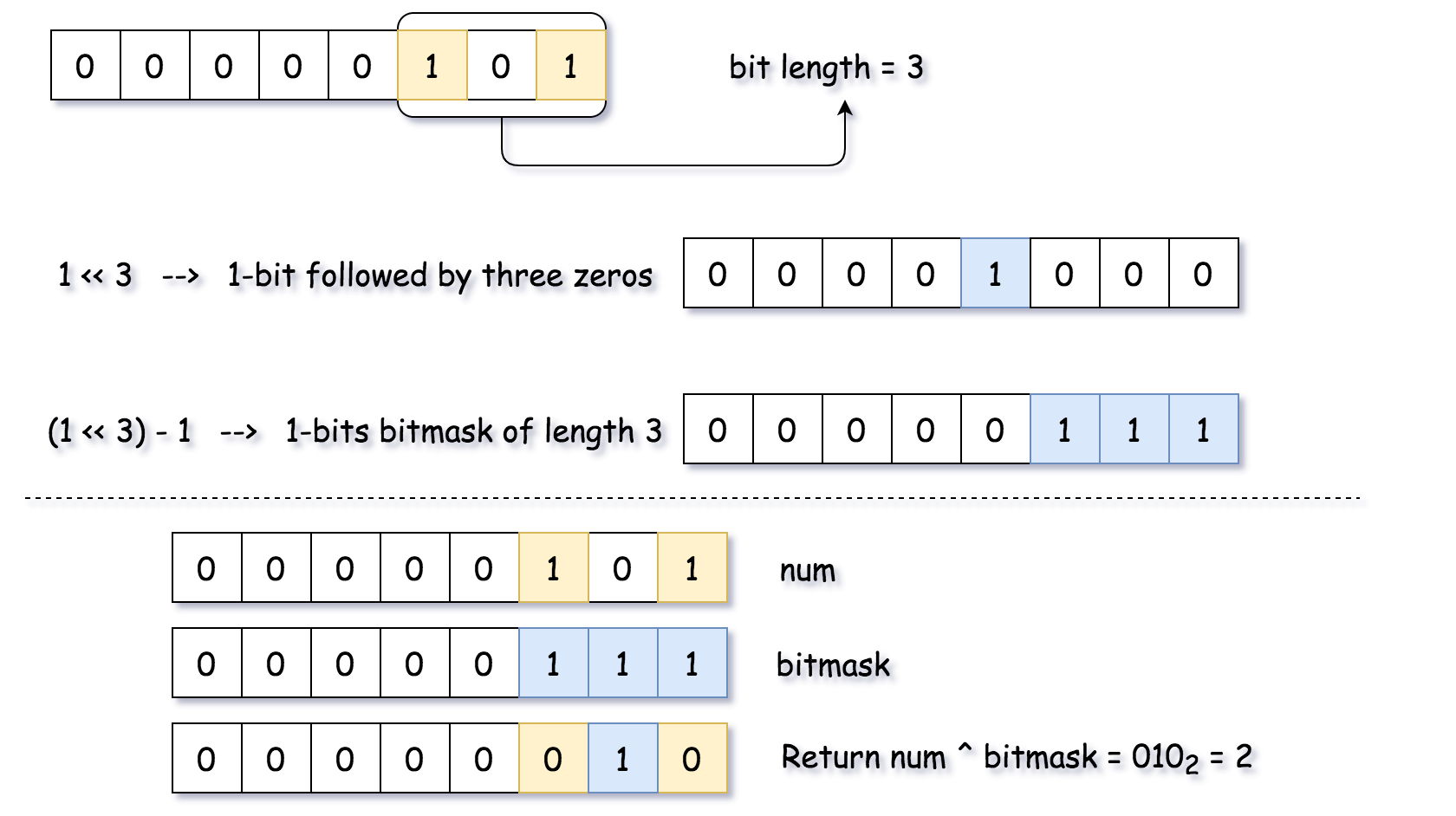 Java
Java
class Solution {
public int findComplement(int num) {
if (num == 0) return 1;
int n = num;
int highest = 0;
// n is a length of num in binary representation
while (n > 0) {
highest++;
n >>= 1;
}
// bitmask has the same length as num and contains only ones 1...1
int bitmask = (1 << highest) - 1;
// flip all bits
return bitmask ^ num;
}
}
Time: O(1)
Space: O(1)
Solution (Built-in Functions to Construct 1-bits Bitmask)
Java
class Solution {
public int findComplement(int num) {
if (num == 0) return 1;
// Integer.highestOneBit(num) return 2^k, k = the highest bit
return num ^ ((Integer.highestOneBit(num) << 1) - 1);
}
}
Time: O(1)
Space: O(1)